The Leading Voices in Food
E203: It works – Chile’s Law on Food Labeling and Marketing
In 2016, the Chilean government implemented a comprehensive set of obesity prevention policies aimed at improving the food environment for children. Results from a multi-year study of that regulation, published in the International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, can now tell us if Chilean children are better off as a result of the policy. Guests on this podcast include: Dr. Gabriela “Gabi” Fretes. She is an Associate Research Fellow at the International Food Policy Research Institute. Dr. Camila Corvalan is the Director of the Center for Research in Food Environments and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases Associated with Nutrition at the University of Chile. And, Dr. Sean Cash is an economist, Associate Professor of Agriculture, Food, and the Environment, and the Bergstrom Foundation Professor in Global Nutrition at Tufts University
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | TuneIN | Google Podcasts | SoundCloud | PocketCasts | Radio Public
Tags: Child Development & Nutrition | Childhood Obesity | Children Food Preferences | Diet & Nutrition | Food Industry Behavior & Marketing | Food Policy | School Meals |

Gabriela (Gabi) Fretes is an Associate Research Fellow in the Nutrition, Diets, and Health (NDH) Unit of the International Food Policy Research Institute. She received her PhD in Food and Nutrition Policies and Programs at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy, Tufts University, USA in 2022 and holds a Masters in Food and Nutrition with a concentration on Health Promotion and Prevention of Non-Communicable Diseases from the Institute of Nutrition and Food Technology, University of Chile. Her research interests are at the intersection of child obesity prevention, food policy and consumer behavior, and her doctoral thesis involved evaluation of a national food labeling and advertising policy designed to improve the healthfulness of the food environment and address the obesity epidemic in Chile, particularly among children. She has worked with a broad range of government, international organizations, academia, public and private sector stakeholders and decision-makers in Paraguay, Chile, and the United States of America.
Camila Corvalán is a surgeon, a Master in Public Health, and holds a PhD in Nutrition. She is the Director of the Center for Research in Food Environments and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases Associated with Nutrition (CIAPEC), at the Public Health Unit of the Institute of Nutrition and Food Technology (INTA) of the University of Chile. CIAPEC is dedicated to the population study of the early nutritional determinants of obesity and associated chronic diseases, particularly metabolic diseases and breast cancer. Their work focuses on carrying out longitudinal epidemiological studies (both observational and intervention) in stages considered critical for the appearance of these diseases, such as pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence, considering various determining factors in both the environment food (set of factors that define population feeding patterns) as individual. CIAPEC is a part of the international network INFORMAS for monitoring food environments, and also carries out policy evaluations such as the Chilean Labeling Law; CIAPEC works in coordination with several governmental bodies.
Sean Cash is an economist and associate professor of agriculture, food and environment at Tufts University. He conducts research both internationally and domestically on food, nutrition, agriculture and the environment. He is interested in the environmental impacts in food and beverage production, including projects on crop quality and climate change, consumer interest in production attributes of tea and coffee, and invasive species management. He also focuses on how food, nutrition, and environmental policies affect food consumption and choice, with specific interest in children’s nutrition and consumer interest in environmental and nutritional attributes of food. He teaches courses in statistics, agricultural and environmental economics, and consumer behavior around food. He is currently Editor of the Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics and on the editorial board of Agribusiness, and has served as the Chair of the Food Safety and Nutrition Section of the Agricultural and Applied Economics Association.
Interview Summary
Sean, let’s set the stage for this conversation. When crafting food policy, what should policymakers consider with respect to children and adolescents, both as current and future consumers in the food system?
I would argue that children and adolescents should be a priority, if not the priority in how we consider dietary policy for a few reasons. In the United States and elsewhere, we often argue quite heatedly about the proper role of government, with the arguments for health-promoting policies seemingly running into conflict with concerns about paternalistic interventions and restrictions on personal choice. These are important and perhaps unavoidable discussions to have. But when it comes to kids, we’ve already long had standards for school meals, what packaged snacks can be sold in schools, etc. We don’t treat children as legally independent in other ways. So while there’s still a lot of room for disagreement, it may be less daunting to actually keep child nutrition in the forefront when we consider how food policies around diet need to evolve. Perhaps more importantly, I would note that food marketers have long seen children as an important three-in-one market. One, kids have influence over food choices within their households. Think of a kid shopping with a parent in a supermarket and pointing at things she’d like mom or dad to buy. We sometimes call this pester power. Two, kids have their own spending money, and much of what they choose to spend it on is food. Often the types of energy-dense, nutrition-poor snack foods that are exactly the foods subject to labeling under the Chilean law we’re talking about today. And three, kids grow up to be adult consumers, and their preferences and knowledge are heavily influenced by the things to which they’re exposed in childhood. For the same reasons that food marketers are interested in children, policymakers should be. Kids have influence in in their households now. They’re buying food on their own now. What they do now will influence their future behaviors and future health.
Thank you, Sean. I have got to say, I went grocery shopping with my child yesterday and I appreciate your thoughts on how we should think about what policymakers should engage, not just in the U.S. but anywhere when we are thinking about helping kids make good choices that will have long-term implications. Thank you for that. I want to turn our attention to the research paper that we’re discussing now, titled, “Changes in Children’s and Adolescent’s Dietary Intake “After the Implementation of Chile’s Law “of Food Labeling, Advertising, and Sales in Schools.” So, Gabi, my question to you is this. One of the key components of the Chilean law was regulating food offerings in schools. Can you explain the focus of that policy and how it is intended to work?
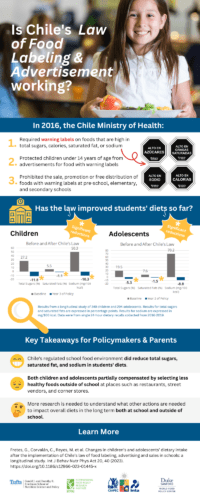
Yes. Before we speak about schools, we should speak about Chile’s law in general. Chile’s law of food labeling and advertising includes three main components. The first one being mandatory front-of-package warning labels on packaged foods and beverages. The second being restrictions on all forms of food marketing directed to children younger than 14 years. The third one is school regulations at the preschool, elementary, and high school levels. Briefly, food manufacturers must place front-of-pack warning labels on packaged foods and beverages that are high in added total sugars, saturated fats, sodium, and energy. This law was implemented in stages starting in June, 2016. The law mandates that food and beverages with at least one front-of-pack warning label cannot be sold, promoted, or marketed inside schools. That includes school kiosks, cafeterias, and events that happen inside schools. Additionally, food and beverages with front-of-pack warning labels cannot be offered as part of the school meals program or as free samples or gifts. Chile’s set of regulations is unique because it includes a package of interventions covering several aspects of the school food environments, such as the availability of foods for sale inside schools, school meal program standards, and restrictions on food marketing directed to children.
Wow, Gabi, this is a very comprehensive law. So what did the team hope to test in the longitudinal study? Could you explain the main findings?
Yes. So with this study, our team aimed to assess if children and adolescents’ intake of total sugars, saturated fats, and sodium consumed at school changed after the initial implementation of the regulation. The team was also interested in exploring how children navigated different food environments. We also evaluated changes in intake at home and different settings from home and school. So, what did we find? Intake of most nutrients of concern, those nutrients under the scope of Chile’s law, including total sugars, saturated fats, and sodium significantly declined at school both for kids and adolescents. At home, we also found significant declines in kids’ total sugar intake, but not changes for adolescents. What makes this more interesting even is that we found evidence of partial compensatory behavior at restaurants, corner stores, street food, among others. Which means that kids and adolescents were consuming less healthy foods outside their school and home.
Thank you, Gabi. I want to now turn to Camila. I’m really curious about this compensatory behavior. The study found this evidence of students compensating somewhat for the healthy foods at school by eating more sugars, saturated fats, and sodium at other locations outside of school. Why do you think this happened?
Norbert, I believe this is a very interesting finding, and there are probably three main reasons why we observed this result in the study. First of all, we know that children, as they age, start to consume much more food from places outside of home. This is something that has been shown previously. We know that when kids start to age, they start to get more sugar, more saturated fat, more energy from restaurants and fast food outlets. This is something that we would expect in a longitudinal study such as the one that we conducted. Secondly, the Chilean law did not include regulation around the schools – so in the neighborhoods that surround the school. This was originally part of the regulation. But, during the discussion and designing, we had to drop this component of the regulation. Basically what we approved is that there were restrictions in the schools, but outside there was no restriction in terms of marketing or the offer of unhealthy foods to children. Finally, it’s likely that the regulation influenced some kids in a positive way. They really changed their behavior. But it’s also possible that other kids did not really change their behavior. Once they had the opportunity of going outside of the school, they just kept buying unhealthy foods with high content of sugar, saturated fat, and sodium.
Thank you so much for that. It does reflect the complexity of the decision patterns that children have in terms of how they eat. I think this is true for all of us. If we are trying to improve in one area, there may be some changes in other areas. But I want to pick up on something you said about why you believe the result occurred the way it did. It had to do with dialogue that went on in Chile about the law. So, I want to ask now, how can we best center the needs and voices of communities in the development of similar regulations? It sounds like some of this happened in Chile. Could you share your thoughts about this?
Yes. So, during the process of developing the regulation in Chile, the Ministry of Health held some participatory discussion throughout the country with families, parents, school teachers, and different stakeholders to actually get their ideas and also assess their concerns about the different components of the regulation. We do believe it’s very important to include the community’s views when we define this kind of policies or programs because what we actually want to modify is people’s behaviors. We really want to understand what is the best way of actually achieving that transformation. We really need to get their view for doing that. In Chile, we did not have a very strong civil society organization that could coordinate these views, and that is why the Ministry of Health had to actively engage the community through participatory dialogues that actually delay a little bit the implementation of the law. But, we believe that certainly strengthened their application.
It’s really interesting to hear about this deliberative process and to see what ultimately came out of that. I want to turn my attention back to Gabi. In the big picture of policymaking, what can we actually learn from Chile’s experience with the food labeling law?
Thank you, Norbert, and I think that we can learn a lot. But, I will highlight three things that we learned from this study. First, I want to say that Chile was the first country in the world that implemented front-of-pack warning labels on packaged foods and beverages high in sugar, sodium, saturated fats, and calories. So, the first thing that I want to highlight is that what’s unique about Chile is that it wasn’t only a labeling regulation but a comprehensive set of actions that included restrictions on marketing as well as school regulations. Food environments as a whole should be conducive to healthier and sustainable diets, and therefore isolated actions would be limited in scope. However, we need to acknowledge that the policy process in Chile was not without complications because there was significant pushback from the food and beverage industry. This is something that countries in the process of designing or implementing similar regulations should expect to happen. They should be prepared to respond with arguments based on evidence. The second highlight is that our results showed that the set of policy interventions may be promising to improve kids and adolescents’ diets at school, but that actions in out-of-school settings should be strengthened to improve overall diets. So for example, I will cite some actions that could complement these regulations, such as the introduction of junk food taxes, the reinforcement of nutrition education in schools and the community, particularly relevant now as we move into the post-COVID-19 era, social marketing campaigns, actions in other settings such as menu labeling in restaurants, improving the availability and acceptability of healthier foods by street vendors, among other actions. And lastly, the third point that I want to highlight is that moving forward, countries should consider equity aspects to overcome structural barriers that limit people’s ability to choose healthier foods and combine mutually-reinforcing strategies to stimulate a holistic food systems response where everyone has access to and can afford healthier foods.
Thank you for those comments, and I really do appreciate this idea of even though this was a comprehensive law, that there are some other spaces that the law could touch on or think about because of the results that we saw with this compensatory behavior. Thank you for sharing that. Sean, my last question is for you. I’m wondering if you could share your thoughts on whether Chile might serve as an example to inform the current front-of-package label discussions we’re having right now in United States.
Oh, absolutely. Chilean law has already served as a model for consideration in many other countries in the region and around the globe, including in our top food trading partner, Mexico, which enacted a Chilean-style labeling law in 2020. Several multilateral health organizations have also expressed support for the Chilean approach to be used elsewhere. And it’s hard to argue against the logic of policymakers in the United States paying close attention to what works well and what doesn’t work in other countries in considering any policies around dietary guidance that we choose to pursue here. But for me, one particularly compelling part of the Chilean law that we should pay attention to in the U.S. is how the standards are consistent, and that the same foods that bear the front-of-pack warning labels are those that are restricted in schools and cannot be marketed to children. Looking for opportunities for similar types of harmonization across different areas of dietary guidance and policy within the U.S. moving forward would certainly help with consumer education, and I think would make sense in other ways. And one interesting thing to keep in mind when talking about the use of mandatory warning labels in a U.S. context is that there are some potentially binding limits on what the government can or can’t compel food manufacturers to put on a food pack. Think of cigarette labels for a moment. We’ve long required that cigarette packages have the rather bland, plain text Surgeon General’s warning that we’re all familiar with seeing. But in the late 2000 aughts, the FDA proposed rolling out a series of graphic warning labels modeled, in part, on similar images used in other countries. And in that case, the effort was scrapped because of a widespread concern that requiring tobacco manufacturers to put a picture of a body in a morgue with a body tag on it, for example, is interpretive language that appeals to an emotional response, and that this would actually be a form of government-compelled speech that runs up against our First Amendment protections in a way that a scientifically-factual, text-only statement would not. While I personally don’t know that the Chilean labels would be interpreted in the same way here, I’m quite certain that legal challenges would be raised to clarify this question in the U.S. context. So, it might be a little bit tougher to take some warning label approaches here in the United States than what we’ve seen enacted elsewhere.
Related Infographic(s)